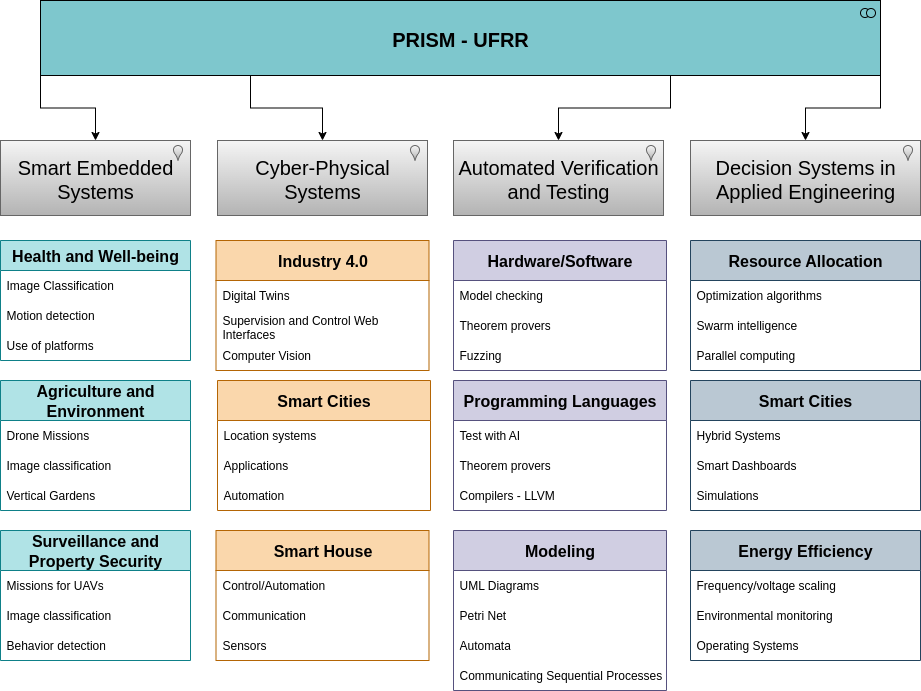
Smart Embedded Systems
Smart Embedded Software refers to embedded systems that incorporate artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) techniques to make autonomous and adaptive decisions. These systems are common in IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, robotics, and industrial automation, where real-time processing with low energy consumption is required.
Related Research Areas:
- Optimization of ML models for resource-constrained devices (e.g., TinyML).
- Real-time processing with low latency in critical embedded systems.
- Edge AI - Running AI algorithms directly on edge devices (edge computing).
Cyber-Physical Systems
Cyber-Physical Systems integrate computing, networks, and physical processes, creating intelligent systems that interact with the real world. They are the foundation for Industry 4.0, smart cities, and critical infrastructures. CPS combine sensors, actuators, software, and communication to monitor and control physical processes.
Related Research Areas:
- Security and resilience in CPS (protection against cyber attacks in critical systems).
- Real-time synchronization and communication in industrial networks (e.g., 5G, TSN).
- Digital Twins - Virtual models that replicate physical systems for simulation and control.
Automated Verification and Testing
Automated Verification and Testing ensure the reliability of electronic and software systems, especially in critical applications (e.g., aerospace, medical, automotive). Techniques such as formal verification, model-based testing, and test automation accelerate fault detection.
Related Research Areas:
- Formal verification of embedded systems (e.g., using model checking and theorem provers).
- AI-based testing (automatic test case generation using ML).
- Testing on reconfigurable hardware (e.g., using FPGAs for rapid prototyping).
Decision Systems in Applied Engineering
Develop and enhance intelligent decision support systems (IDSS) applied to complex engineering problems, combining artificial intelligence (AI), optimization, data science, and computational modeling techniques to assist in technical, operational, and strategic decision-making in industrial, logistics, energy, and infrastructure contexts.
Related Research Areas:
- Modeling and Simulation for Engineering Decisions - Development of mathematical models and agent-based simulations to predict scenarios in complex systems (e.g., supply chains, energy networks, urban traffic).
- Optimization and Algorithms for Autonomous Decisions - Application of multi-objective optimization algorithms (e.g., genetic algorithms, swarm intelligence) in resource allocation, routing, and production management problems.
- Hybrid Decision Support Systems (Human-in-the-Loop) - Development of intelligent dashboards with predictive and prescriptive analytics for engineers and managers.
PRISM Projects
Ongoing projects:
Map2Check
An automated method for checking safety properties for programs written in C.

Kraken
Autonomous system for detecting and estimating objects submerged in water.

GAN-AGE
A system for generating temporal prediction-based images to missing persons.
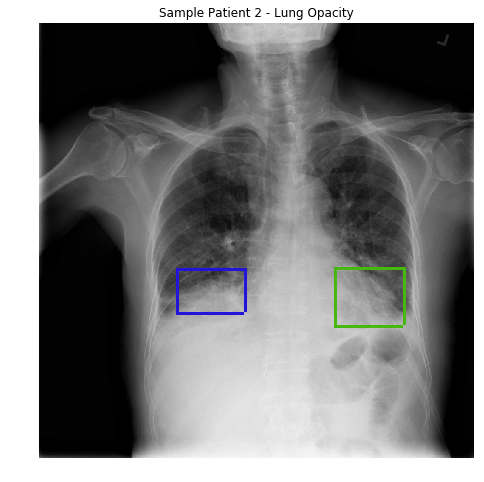
Xray-Vision
Diagnosis of Childhood Pneumonia Using Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Pattern Recognition in X-Ray Images.